
Urine incontinence, which is one of the diseases that are difficult to treat due to the fact that it is made under the mat and not intervened in time, is the loss of urinary bladder control in the sense of involuntary drops or more intense leakage of urine. Made works; Reveals that 24 percent of women older than 18 years have missed urine. This is seen in 15 percent of young adults, while in the 70s to 50 percent.
Urinary incontinence is a health problem that is often hidden but not shared with the closest ones because it is seen as a ”shame da in society, or seen as a natural consequence of old age. However, the problem grows over time and becomes a social problem that keeps women away from society, causing them to live withdrawn. Previously, the woman who managed the situation by using a pad, over time, first to travel away, then give up going to closer visits. He cannot spend a long time away from home and the toilet and is slowly isolated from society.
Urinary Incontinence Types
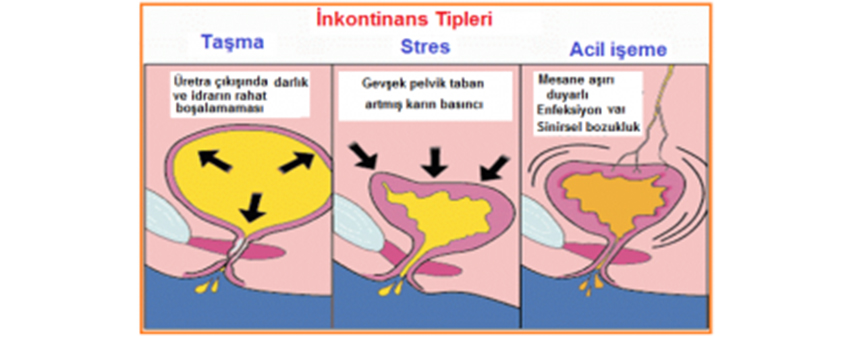
Stress urinary incontinence: It is the most common type of urinary incontinence in women. Urine is missed during various movements such as coughing and exercise. as a result of sagging of the bladder and its attachments and usually undergoes a surgical procedure.
Urge incontinence (urge incontinence): Urine incontinence when a strong and urgent need to go to the toilet is felt.
Mixed Type Urinary Incontinence: Mixed urinary incontinence is mentioned when stress urinary incontinence is combined with urge incontinence. For example, when a patient coughs or sneezes, sometimes they may miss urine after a sudden feeling of urgency.
Overflow urinary incontinence: When urine is stored above the capacity in the bladder, a small amount of urinary incontinence occurs without the need to urinate. The patient feels that he can never empty his bladder completely.
Total Urinary Incontinence: The patient states that he does not notice that he has missed urine and that his underwear is wet.
Functional Incontinence: In some patients, despite the incontinence problem, the examinations are normal. This group of patients has causes such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's or arthritis.
What are the reasons for incontinence?
Bladder infections (cystitis), genital organ infections, bladder stones, tumors, especially bladder outlet obstructions due to enlargement in men can cause overactive bladder. Among the reasons that may cause continuous urinary incontinence in women are pathological pathways called fistula between bladder and vagina.
Overflow Type Urine Incontinence can cause nerve damage, including diabetes, alcoholism.
In children, nocturnal or daytime (diurnal) incontinence is called enuresis. Spinal cord impingement can lead to neural incontinence and dysfunction in children; constipation may pave the way for infection and urinary incontinence.
Various operations in both sexes may cause urinary incontinence. Other prostatic and bladder neck surgeries in men, especially for cancer of the prostate, and sphincter that prevent urinary incontinence in women may cause failure of the region can be counted among other incontinence.
Medications can also cause or facilitate urinary incontinence: muscle-relaxing drugs, blood pressure-lowering drugs, diuretics, tranquilizers, anti-depression drugs, allergy drugs, such as drugs.
Diagnosis of Urinary Incontinence
In the treatment of urinary incontinence, determining the type of incontinence is of great importance for treatment. In addition to the examination, your doctor may ask you for some tests to confirm the diagnosis of incontinence. Tests are of paramount importance for the proper treatment. These tests include:
HOW IS URINE INCIDENCE TREATED?
The most appropriate treatment will be determined by the type of incontinence. Because not every treatment approach may be effective in all types of urinary incontinence. Treatment alternatives include:
Kegel exercises
Exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles within the groin area are effective in some cases alone but generally as an adjunct method. With this treatment, the bladder and the muscles related to urination are controlled and the pelvic floor muscles are strengthened. In addition to these exercises, a diary (urine diary) is created to provide bladder training under this program. Electrical stimulation with or without biofeedback is also effective in strengthening weakened pelvic floor muscles.
Medication
Some types of urinary incontinence are treated with drugs or hormones. Especially in urge urinary incontinence drug treatment is the first choice. The duration of drug therapy varies from patient to patient.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is performed when other treatment approaches fail. Nowadays, new methods which are very simple, less invasive (with less incision), which can be applied even under local anesthesia, can be applied in a very short period of time, and with shorter periods of discharge and recovery are applied. TOT (Transobturator Tape) method is the latest technology and is based on the prevention of escape with a body-friendly substance wrapped around the urinary tube, the patient is sent home without probes on the same day or the following day.
Injections Around Urethra
Various substances are injected under the local anesthesia around the urine pipe in patients who cannot have surgery or will not benefit. These are collagen, silicon, botox, polytef or macroplasty called different protein or chemical substances.
Botox Injections
In this very new method, botulinum toxin is injected into the bladder muscles to provide temporary relaxation in the muscles of the bladder so that urgent urinary incontinence or incontinence is tried to be treated.
WHEN TO CONSULT A DOCTOR?
If you answer “yes ine to one of the following questions, consult a Urologist.